What’s Brewing: Caffeine
Caffeine and performance
By definition caffeine, as a nutraceutical, can have a negative and positive effect upon one’s body depending on the dose and one’s metabolism

"Cup of Joe"
Almost everyone is familiar with caffeine. Many of us rely on a good cup of “Joe” in the morning to jump start our bodies or help give us a pick-up during the day. Then we read with dismay the various — sometimes conflicting — information stating that caffeine may not be good for our health, let alone our athletic performance.
What is it...
Although caffeine is a common ingredient in many beverages, foods, and over-the-counter medications, perhaps it can no longer be classified as a food or a drug. Dr. Jeffrey Bland, of HealthComm, Inc., a company specializing in health and nutrition education, says caffeine falls into a recently defined in-between category called nutraceuticals. A nutraceutical is a food-derived substance that can have pharmacological effects on the body.
Caffeine fits this description perfectly.
By definition, caffeine, as a nutraceutical, can have a negative and positive effect upon one’s body, depending on the dose and one’s metabolism.
Many athletes already know that in moderate doses caffeine can have a positive effect upon performance


Performance
While cycling, your muscles are using some combination of carbohydrate and fat for fuel. As you increase the intensity of your effort, there is a tendency for your muscles to use a greater proportion of carbohydrate as a fuel.
However, when you consume caffeine in the form of cola, coffee, or tablets, stored fat is made available to your muscle cells. This, in turn, causes a switch from using stored glycogen as the preferred fuel to using more of the free fatty acids that caffeine helps provide. The result is the sparing of glycogen, one of the two major energy sources for muscle cells during exercise, thereby making it available for the final climb or sprint in the race.
Dose
Two milligrams of caffeine per pound of your body weight taken about 30 to 60 minutes before exercise may provide an optimal dose before long road races or criteriums.
For reference, a cup of drip coffee has approximately 125 milligrams of caf-feine, a cup of instant coffee about 100 milligrams, and soft drinks from 30 to 60 milligrams, A 170-pound cyclist, therefore, could consume about three and a half cups of coffee and possibly notice an ergogenic effect.
At these levels of ingestion, however, caffeine’s diuretic effect causes increased loss of water through the urine 30 minutes to two hours after ingestion, which may dangerously compound your loss of water during long races. Also, caffeine-induced acid secretion in the stomach may lead to heartburn.


Evidence
In addition, there has been evidence published showing that excessive and chronic use of caffeine can lead to episodes of anxiety and high-blood pressure. It has also been proven that when caffeine is taken in high doses, some subjects performed worse than when they were given a placebo. Taken in excess, caffeine can also irritate one’s stomach lining, disrupt sleep, cause diarrhea, and accelerate dehydration. These are all race-day problems that racers certainly don’t need.
Caffeine may also have other physiological benefits. Road racers have been known to consume a small amount of espresso near the end of a race, and some sprinters drink strong coffee prior to track competitions. These athletes are hoping to take advantage of caffeine’s effects on the central nervous system. Caffeine has been shown to help reduce the sense of physical effort one experiences during hard exercise. Some people claim that caffeine stimulates the brain, thereby increasing alertness, In addition, caffeine may be linked to the release of calcium in the muscles. which initiates muscle contraction.
In a recent study on caffeine use and motor reactions, scientists lested three separate groups. The first group ingested 300 milligrams of calfeine, the second group 600 milligrams, and the third group, serving as a control, no caffeine. The 300-milligram group reported the fastest reaction times. A surprise to the research team was that the 600-milligram group reacted no faster than the control group. The results indicate that although some caffeine may boost performance, too much may prove ineffective.
Program
Finally, habitual coffee or soda drinkers usually build up a tolerance to caffeine, which reduces side effects such as nervousness, increased heart rate and increased urination, as well as any improvement in performance It you are accustomed to high levels of coffee or caffeinated beverages and you try to back off, you might even experience withdrawal symptoms such as headache, nausea, or lethargy
If you can wean yourself from caffeine for a few days before a race. however, caffeine may give you a lift on race day. One recent study examined the results of giving caffeine to coffee-drinking athletes after they had abstained from caffeine for four days prior to a more. The research team found that blood levels of free fatty acids were greater following the with drawal from caffeine than they were when the athletes stuck to their regular caffeine babits. These results imply that you may gain a greater benefit from caffeine if you don’t regulars drink heverages that contain it of if you abstain for a few days.
The botom line is that caffeine is a plant-derived nutraceutien that can have pharmacological effoets upon the body. Some of the effects are beneficial, while others, in excess, can be harmful. As with all things related nutrition, each individual should evaluate caffeine’s effects upon his or her body and, if the decision is made to use caffeine, consume it at levels that take advantage of is beneficial effects but minimize the adverse effects of excess intake.
BY EDMUND R. BURKE, PH.D.
Winning, May 1996

Simple Training Camp and Race Nutrition Plan
Food for Sport
A straightforward nutrition plan to keep you energized and performing your best during long training sessions or competitions.


Breakfast
- Porridge oats or cereals
- Tea or coffee (coffee-latte not recommended)
- Yoghurt or ricotta
- Ham crisp breads
- Freshly squeezed fruit juice
- Honey/marmalade on toast
Lunch
After training ride, before massage
- Vegetable salad with olive oil
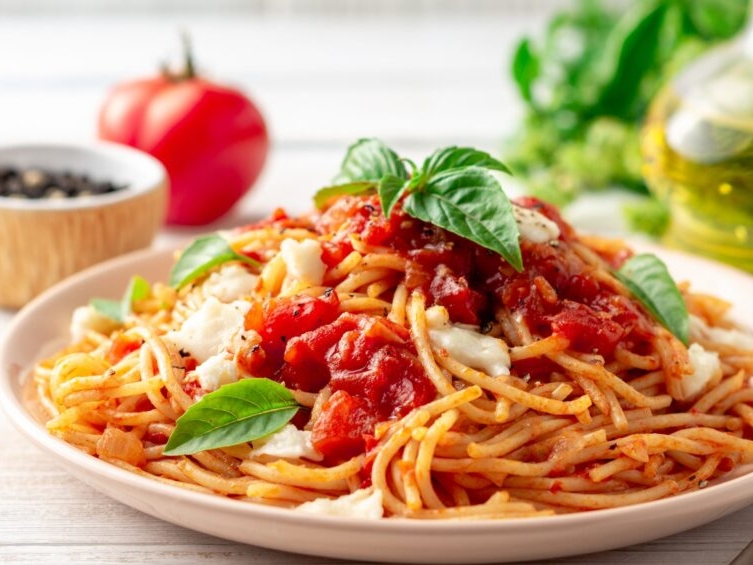
- Spaghetti with fresh tomato Sauce
- Fresh cheese or ham
- One slice of torte della gonna (Fruit tart)




Snack
- Fruit juice
- Cereal bars
- Fresh Fruit (not with 2 hours of meal times)
Evening Meal
- Vegetable salad with olive oil
- chunky minestrone soup, or past with olive oil
- Two pieces of meat, fish or cheese
- Vegetables: Lentils, chick peas, beans
- Sweet




Race Nutrition Plan
Complete meal 3-4 hours prior to race
- Plate of pasta with olive oil
- Green salad dressed with olive oil and lemon juice
- Cheese
- Yogurt
- One slice of fruit tart
Note: Its preferable not to drink during the meal, but to drink a small cup of black coffee shortly afterwards
Pre-Race Snack (very important)
- Half glass composed in equal parts of fruit juice, or iced tea, or water and honey!
- This should be consumed regularly, every half-hour, up to 15 minutes before the race begins.




During Race
GUIDELINES: A rider can “survive” without eating in a race for 2 to 3 hours. However, given that it takes approximately 2 to 3 hours for food to release energy to the muscles, it’s advisable to begin eating immediately after the start of the race. Food must not impede chewing and salivation, and should be proportionate to energy consumed during the race.
RECOMMENDED: Crisp breads with honey and jam; carbohydrate-based energy bars; small bread rolls with honey or cheese; water; iced tea
After Race
Large quantities of liquid, for rehydration: cool, sparkling mineral water then, after a shower and massage, skimmed milk, Finally, water with added mineral salts 30 minutes before evening meal.




Evening Meal
- Chucky minestrone, potatoes. pasta, or rice dressed with olive oil and lemon juice
- One yoghurt or low fat cheese
- One piece of fruit
- One glass of pasteurized milk before going to bed
Tools of the Kitchen
Tools of the Kitchen
Good nutrition begins with cultivating the right environment and ensuring your kitchen is equipped with the proper tools.


Cutting Board
Look to have a high quality wooden cutting board. With all the fruit and vegetables to chop, it’s essential to have the right surface to work on.
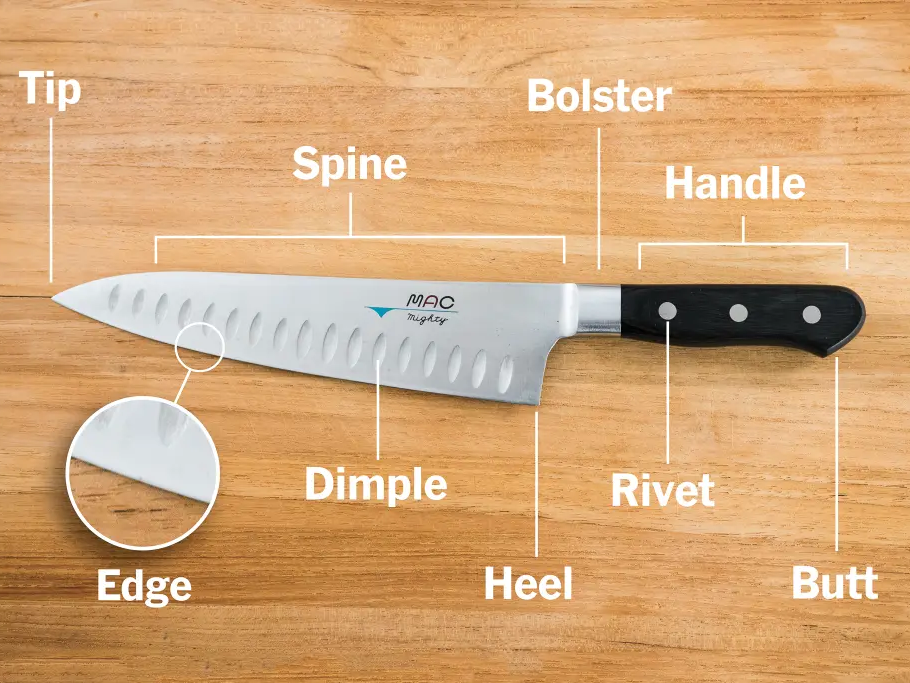
Cheifs Knife
To accompany your cutting board, look to invest into a chefs knife. This knife is very versatile, easy to use and make easy work in the kitchen.
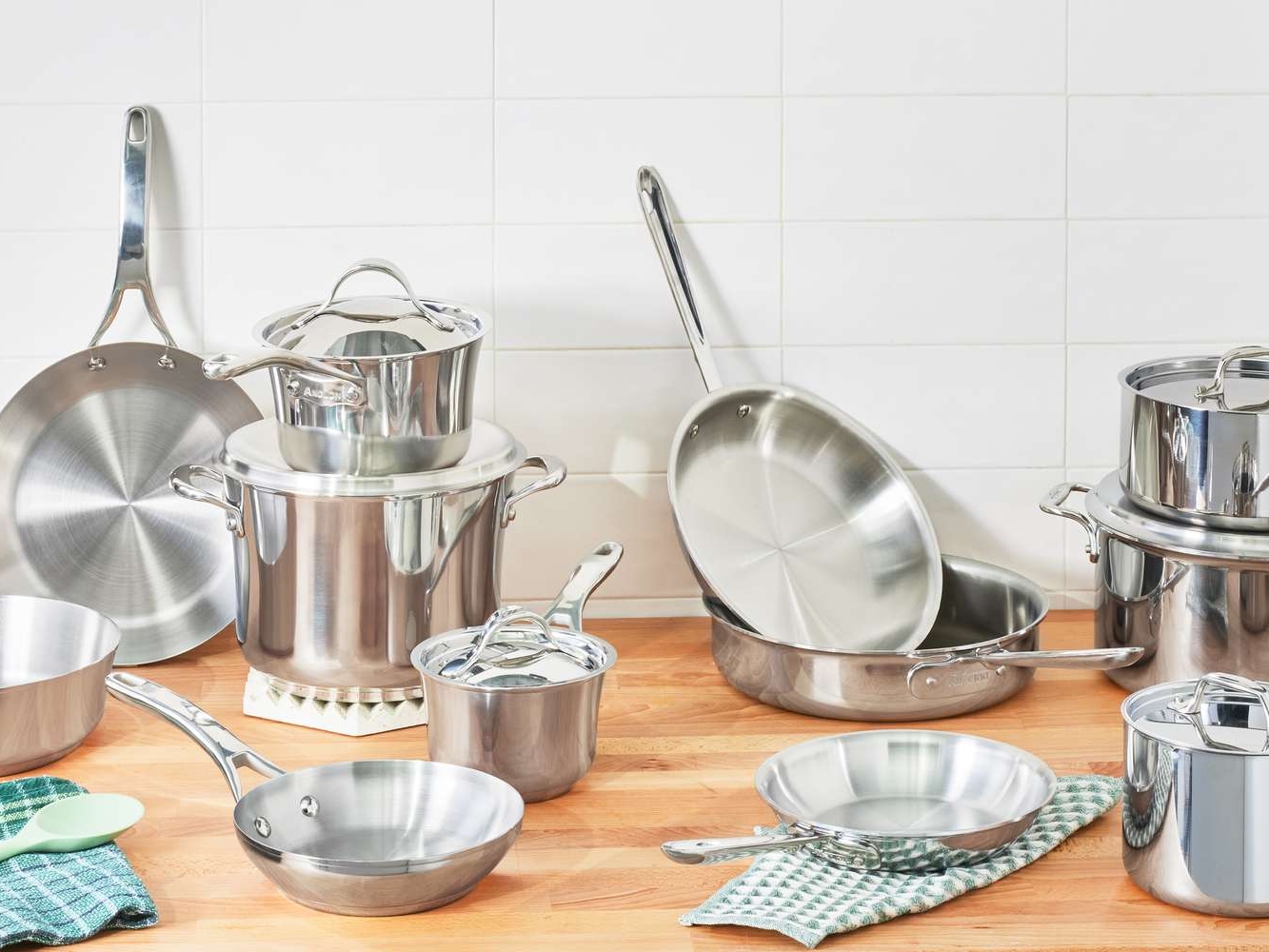



Pots and Pans Cookware
For all your cooking needs it’s a must to have a set of stainless steal pots and pans. Look to start with a few standard sizes of each and add as you advance your cooking skills
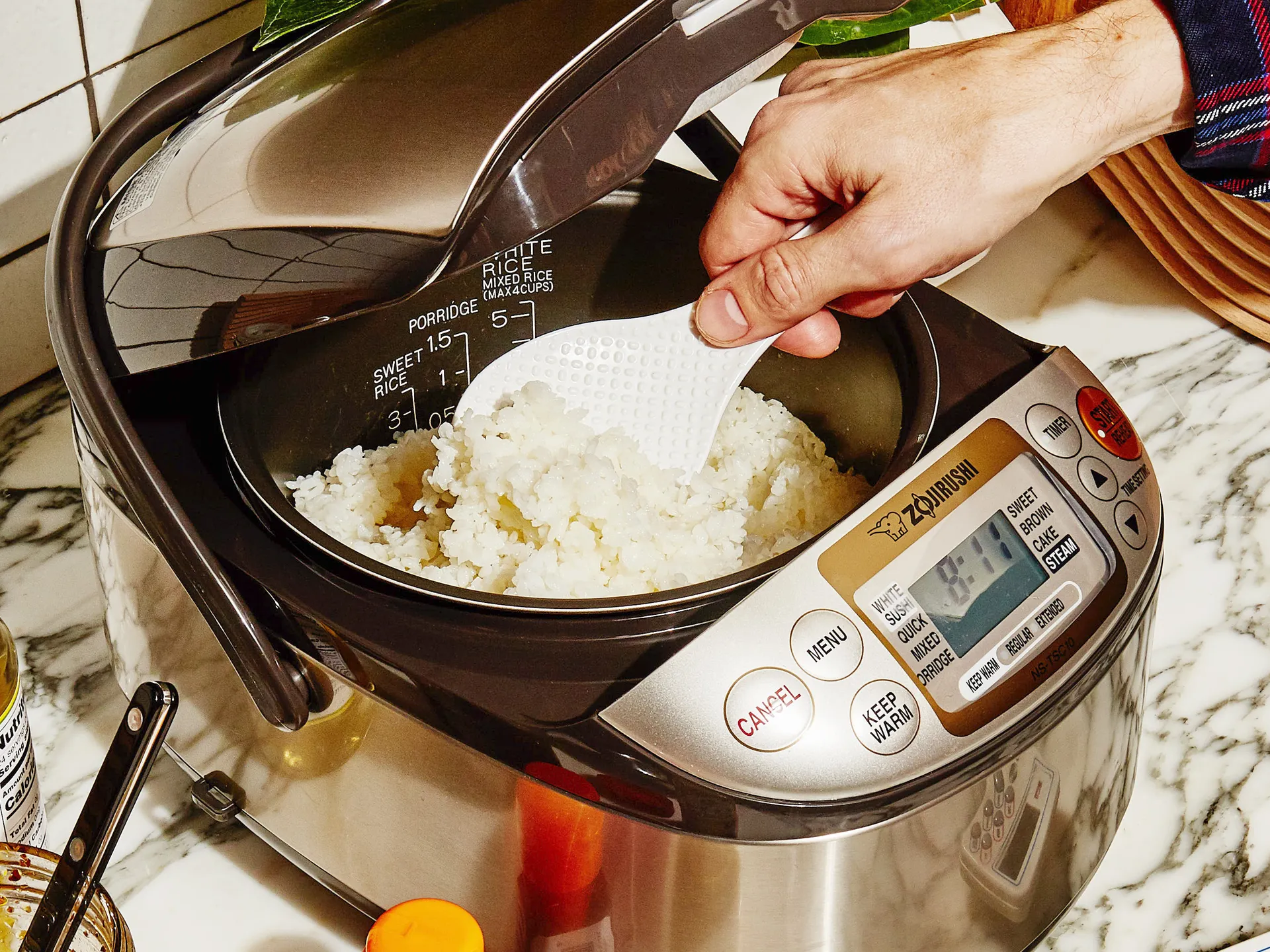
Rice Cooker
As endurance athletes we need and love our carbs! To make things easier and have the ability to cook in large quantities, look to add a rice cooker to the kitchen.
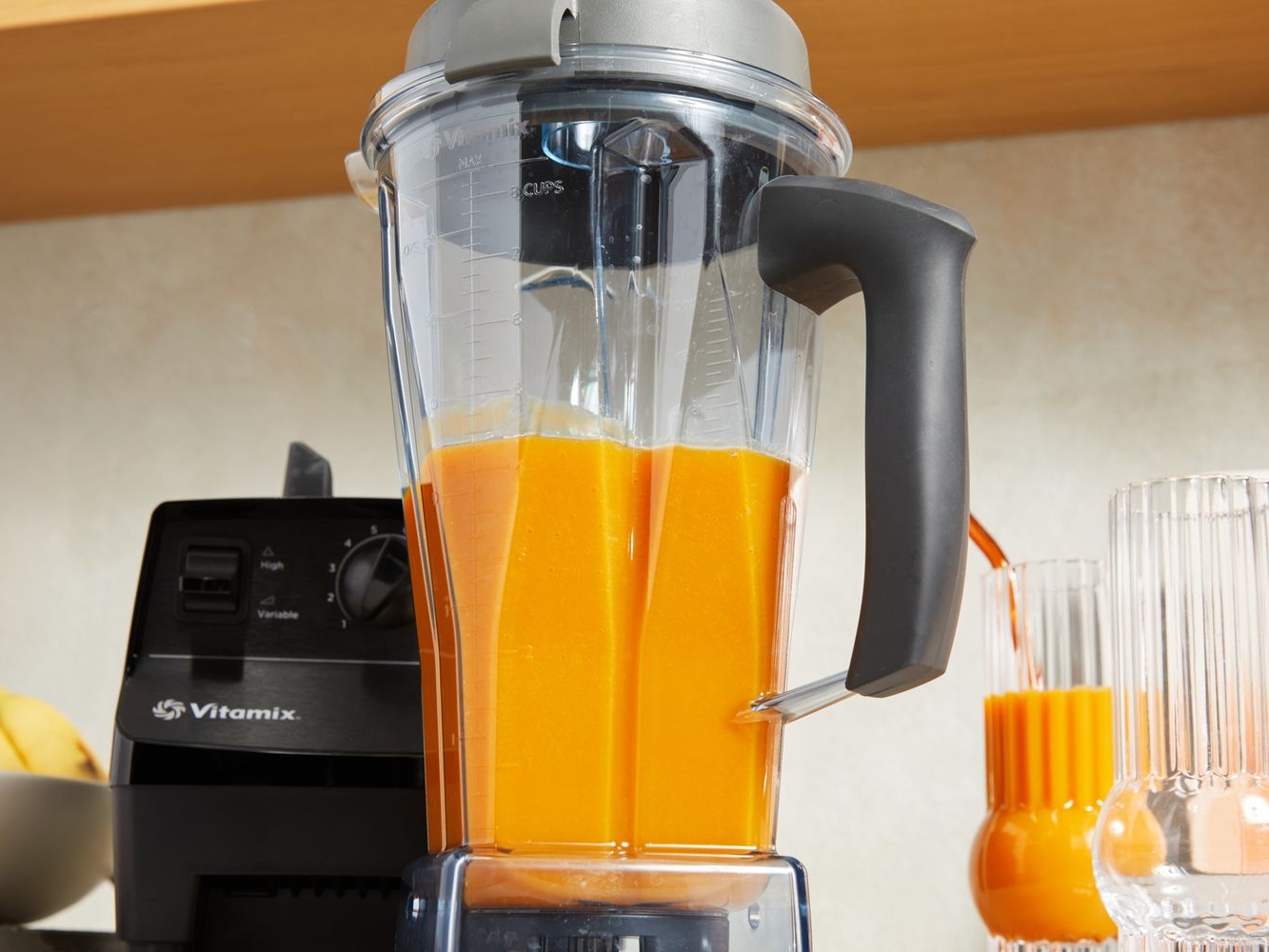




Blender
As an athlete one of the most important tools is a good blender. Recommended is the Vitamix brand for its high power and many features. Make sure to have a blender and not a juicer to retain the fiber content of smoothies.
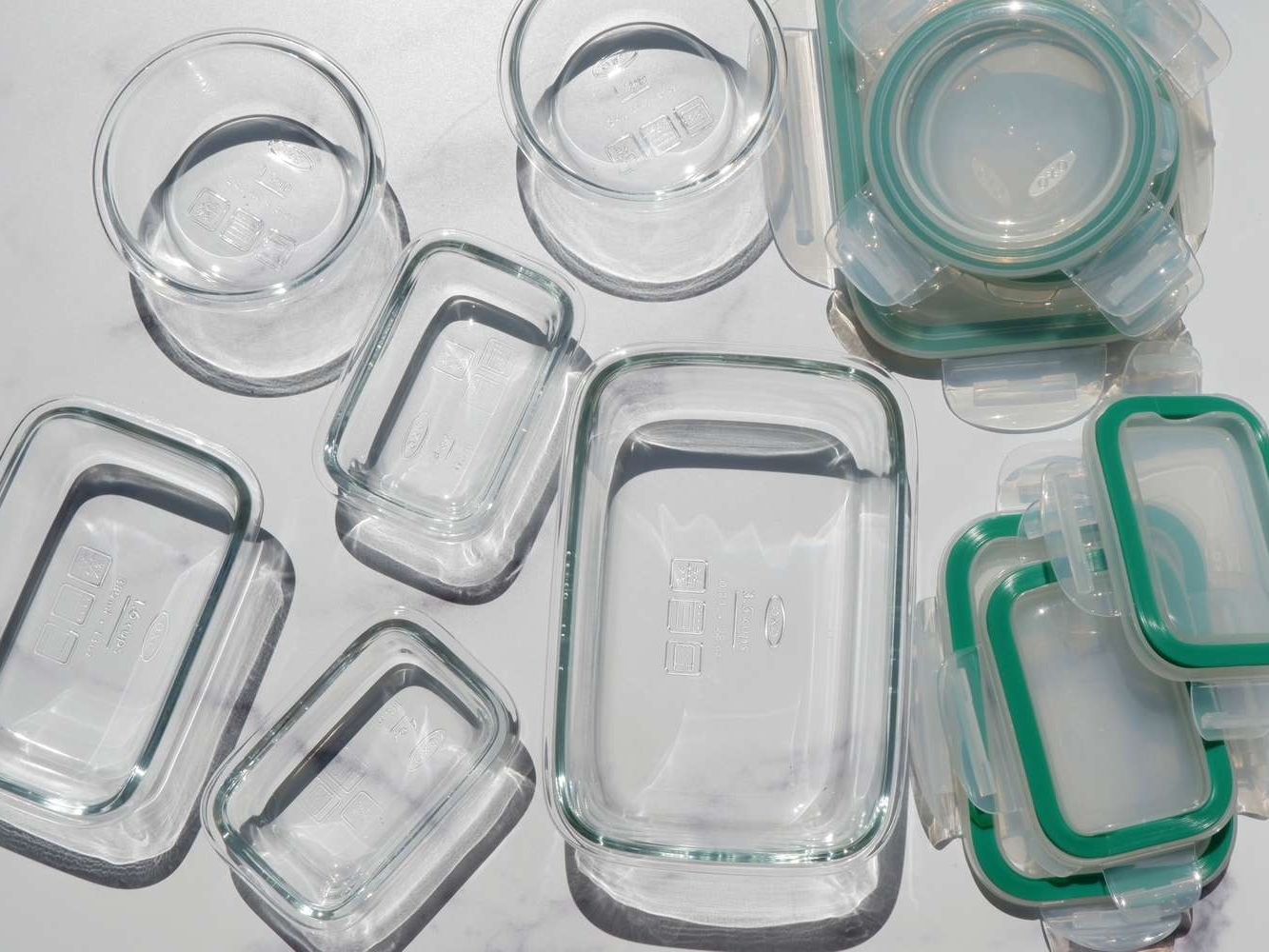
Glass Storage Food Containers
Purchase some glass storage containers to store food properly, meal plan with cooking in advance and have foods ready for travel.
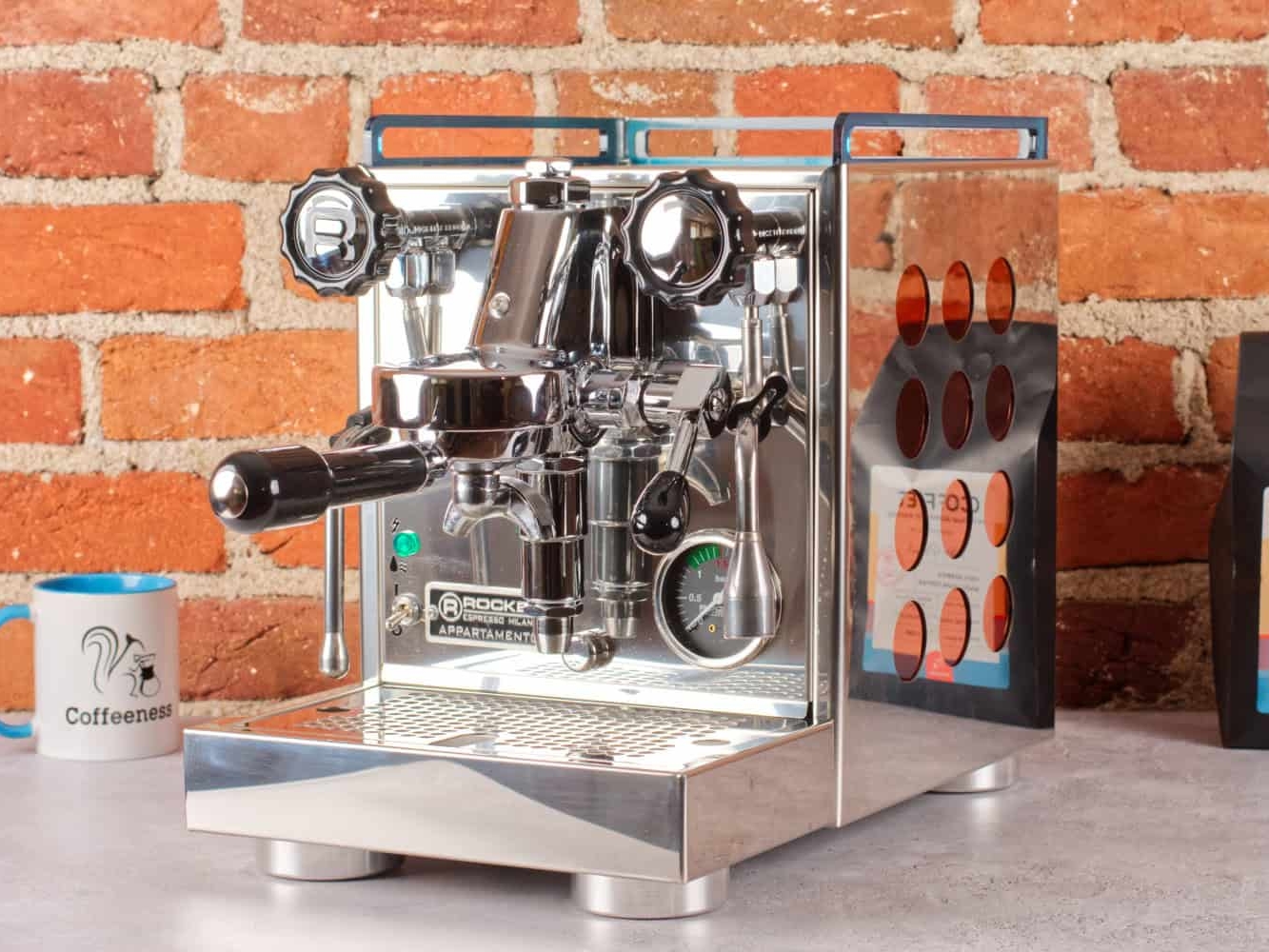




Espresso or Coffee Machine
For a treat or to get a bit of energy, look to add an espresso or coffee machine to the kitchen. Great to wake you up or increase your endurance on long training sessions. Coffee is the drink of choice.
Grinder
For adding herbs and spices to your dish, have a grinder on hand. Not only for the health benefits of these types of seasoning, but to enhance the flavor of your meals.




Tea Kettle
A must is the tea kettle in the kitchen. Whether you enjoy a warm cup over other choices or you want the performance gains from it. The most popular choice around the world is tea! Look to consume green tea in the morning, during or after training and even throughout the day. This beverage is low in caffeine, will warm you up on cold day, or help with health and weight management from the polyphenol properties of herbal teas.
Peeler
To speed cooking up, you will want to have a peeler to remove roughage from vegetables. Always convenient when cooking to reach for the peeler.


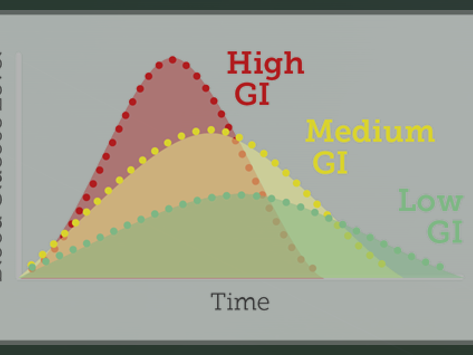
Glycemic Index
Glycemic Index
What to Know About and How to Use a Glycemic Index


The glycemic index (GI) is a value used to measure how much specific foods increase blood sugar levels.
Foods are classified as low, medium, or high glycemic foods and ranked on a scale of 0–100.
The lower the GI of a specific food, the less it may affect your blood sugar levels.
Here are the three GI ratings:
- Low: 55 or less
- Medium: 56–69
- High: 70 or above
Digestion/Factors/GI vs GL
Foods high in refined carbs and sugar are digested more quickly and often have a high GI, while foods high in protein, fat, or fiber typically have a low GI. Foods that contain no carbs are not assigned a GI and include meat, fish, poultry, nuts, seeds, herbs, spices, and oils.
Other factors that affect the GI of a food include the ripeness, cooking method, type of sugar it contains, and amount of processing it has undergone.
Keep in mind that the glycemic index is different from the glycemic load (GL).
Unlike the GI, which doesn’t take into account the amount of food eaten, the GL factors in the number of carbs in a serving of a food to determine how it may affect blood sugar levels.
For this reason, it’s important to take both the glycemic index and glycemic load into consideration when selecting foods to help support healthy blood sugar levels.


Low GI Foods
A healthy, low glycemic diet should comprise mostly of:
- Fruits: apples, berries, oranges, lemons, limes, grapefruit
- Non-starchy vegetables: broccoli, cauliflower, carrots, spinach, tomatoes
- Whole grains: quinoa, barley, buckwheat, farro, oats
- Legumes: lentils, black beans, chickpeas, kidney beans




Foods very low or without a GI value
Foods without a GI value or with a very low GI can also be enjoyed as part of a balanced low glycemic diet. They include:
- Meat: beef, bison, lamb, pork
- Seafood: tuna, salmon, shrimp, mackerel, anchovies, sardines
- Poultry: chicken, turkey, duck, goose
- Oils: olive oil, coconut oil, avocado oil, vegetable oil
- Nuts: almonds, macadamia nuts, walnuts, pistachios
- Seeds: chia seeds, sesame seeds, hemp seeds, flax seeds
- Herbs and spices: turmeric, black pepper, cumin, dill, basil, rosemary, cinnamon
- Some pastas: Semolina and whole grain pasta
Foods with a High GI:
- Bread: white bread, bagels, naan, pita bread
- Rice: white rice, jasmine rice, arborio rice
- Cereals: instant oats, breakfast cereals
- Starchy vegetables: mashed potatoes, potatoes, french fries
- Baked goods: cake, doughnuts, cookies, croissants, muffins
- Snacks: chocolate, crackers, microwave popcorn, chips, pretzels
- Sugar-sweetened beverages: soda, fruit juice, sports drinks


Fruits
- Apples: 44
- Strawberries: 40
- Dates: 55
- Oranges: 45
- Banana: 62
- Mango: 60
- Blueberries: 53
- Pineapple: 66
- Watermelon: 50




Vegetables
- Carrots (boiled): 32
- Plantains (boiled): 66
- Sweet potatoes (steamed): 71
- Pumpkin (boiled): 75
- Potatoes (boiled): 87
Grains
- Barley: 28
- Quinoa: 50
- Rolled oats: 57
- Couscous: 70
- Popcorn: 70
- Brown rice: 79
- White rice: 70
- Whole wheat bread: 73
- White bread: 81




Legumes
- Soybeans: 16
- Kidney beans: 26
- Chickpeas: 33
- Lentils: 37
Dairy products and dairy alternatives
- Soymilk: 41
- Skim milk: 37
- Whole milk: 41
- Ice cream: 62
- Rice milk: 79




Sweeteners
- Fructose: 23
- Coconut sugar: 54
- Maple syrup: 54
- Honey: 59
- White sugar: 91
Macro Nutrient Meal Plan: Prep Phase
Prep Phase Macro Nutrient Meal Plan
Look to modify diet to equal these Macro ratios:
Carbs: 40-45%Protein: 15-20%
Fat: 35-40%





Super Water
Upon waking: : 6:00-7:15 am
Ingredients: 12-160z glass of water. In addition add all or any of the following: salt, squeeze of lemon, chia seeds, apple cider vinegar, & local honey
Breakfast
Within 45 minute upon rising look to consume breakfast. Breakfast options are:
Avocado and Tofu toast would be consumes on most training day. Within this phase I would still look to consume the Oatmeal 2-3 times per week.










Coffee and Green Tea
With or around breakfast add liquid intake with:
1 Double Espresso or cup of Americano Coffee
and
1 cup 6-8oz of Green Tea
Training
Start training 1 to 2 hrs after finishing breakfast
(9:30-10:00am)
During this phase look to consume what you like to eat during each hour of training according to your personalized activity burn rate.
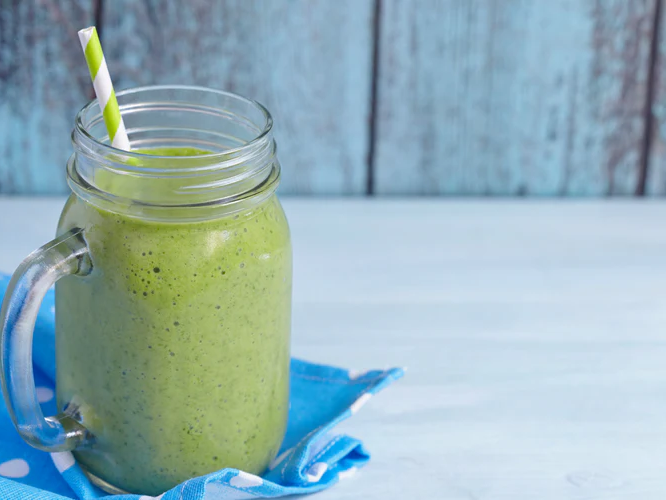










Recovery Shake: Post Training
Consume immediately after completion of training. Options include:
Lunch
Lunch should be a balanced meal with a vegetable base during this phase of training.
Options include:
Large salads with seeds, nuts, hummus
Bean Salad








Dinner
Diner should focus on a balance meal including carbohydrate, protein and fat source. Start with vegetable minestrone soup.
Options include:
Budda Bowel
Chicken, rice, broccoli
salmon, sweat potatoes, cauliflower salad











Evening Snack
Evening snack must be consumed no later than 2 hrs before plan sleep time.
Snacks include:
Fruit dish
Protein Shake
personal choice
Also, look to complete any macro nutrients deficinces that have not been complete for the day.
Liquids
In addition to consuming liquids during training and during meal times. Make sure to take in adequate amounts of water throughout the day.
Reference your personalized hydration schedule but in general look to consume 64-82 ox of water multiply times per day at 8-16oz increments.





Macro Nutrient Meal Plan: Base Phase
Base Phase Macro Nutrient Meal Plan
Look to modify diet to equal these Macro ratios:
Carbs: 35-40%Protein: 15-20%
Fat: 40-45%





Super Water
Upon waking: : 6:00-7:15 am
Ingredients: 12-160z glass of water. In addition add all or any of the following: salt, squeeze of lemon, chia seeds, apple cider vinegar, & local honey
Breakfast
Within 45 minute upon rising look to consume breakfast. Breakfast options are:
Avocado and Tofu toast would be consumes on most training day. Within this phase I would still look to consume the Oatmeal 2-3 times per week.










Coffee and Green Tea
With or around breakfast add liquid intake with:
1 Double Espresso or cup of Americano Coffee
and
1 cup 6-8oz of Green Tea
Training
Start training 1 to 2 hrs after finishing breakfast
(9:30-10:00am)
During this phase look to consume trail mixes, nut or seed bars, small nut-butter sandwiches, dates, and bananas each hour of training according to your personalized activity burn rate.










Recovery Shake: Post Training
Consume immediately after completion of training. Options include:
Lunch
Lunch should be a balanced meal with a vegetable base during this phase of training.
Options include:
Large salads with seeds, nuts, hummus
Bean Salad








Afternoon Snack
Look to snack on some fruits and vegetables. Other snacks include, edamame, trail mixes including nuts and seeds.
Dinner
Diner should focus on a balance meal including carbohydrate, protein and fat source. Start with vegetable minestrone soup.
Options include:
Budda Bowel
Chicken, rice, broccoli
salmon, sweat potatoes, cauliflower salad











Evening Snack
Evening snack must be consumed no later than 2 hrs before plan sleep time.
Snacks include:
Chia Pudding with toping
Protein Shake
Also, look to complete any macro nutrients deficinces that have not been complete for the day.
Liquids
In addition to consuming liquids during training and during meal times. Make sure to take in adequate amounts of water throughout the day.
Reference your personalized hydration schedule but in general look to consume 64-82 ox of water multiply times per day at 8-16oz increments.





Macro Nutrient Meal Plan: Specialization Phase
Specialization Phase Macro Nutrient Meal Plan
Look to modify diet to equal these Macro ratios:
Carbs: 55-60%Protein: 15-20%
Fat: 20-25%





Super Water
Upon waking: : 6:00-7:15 am
Ingredients: 12-160z glass of water. In addition add all or any of the following: salt, squeeze of lemon, chia seeds, apple cider vinegar, & local honey
Breakfast
Within 45 minute upon rising look to consume breakfast. Breakfast options are:
- Super Oatmeal
- Rice with sea salt and honey
- French Toast
Oatmeal would be the go to on tough or high volume days of training, with Rice and French Toast dishes for competition or competition like training days.










Coffee and Green Tea
With or around breakfast add liquid intake with:
1 Double Espresso or cup of Americano Coffee
and
1 cup 6-8oz of Green Tea
Training
Start training 1 to 2 hrs after finishing breakfast
(9:30-10:00am)
Look to consume simple carbohydrates in the form of liquids, bars, gels, gummies, etc each hour of training according to your personalized activity burn rate.










Recovery Shake: Post Training
Consume immediately after completion of training. Options include:
Lunch
Lunch should be a balanced meal focused on carbohydrates during this phase of training.
Options include:
Bean Salad
Pasta with Vegetables









Afternoon Snack
Start off with a small sandwich such as
In addition add snacks of fruits and vegetables. Other snacks include, whole grain cereals, trail mixes including nuts and seeds.
Dinner
Diner should focus on a balance meal with a carbohydrate base and include a protein source and fat source.
Options include:
Budda Bowel
Rice and pasta dish with chicken and vegetables











Evening Snack
Evening snack must be consumed no later than 2 hrs before plan sleep time.
Snacks include:
Chia Pudding with toping
Protein Shake
Also, look to complete any macro nutrients deficinces that have not been complete for the day.
Liquids
In addition to consuming liquids during training and during meal times. Make sure to take in adequate amounts of water throughout the day.
Reference your personalized hydration schedule but in general look to consume 64-82 ox of water multiply times per day at 8-16oz increments.





Supplement Guide (Pills & Powders)
Supplement Guide (Pills & Powders)
How to read this guide
This guide is to help you with incorporating nutrition needs in addition to regular food intake. If needed, look to ingest these supplements including vitamins and minerals around your meals and workout sessions during the day. Make sure to cycle these supplements according to the detail below.
Vitamins & Minerals


Breakfast
- Before Breakfast: Take during season 20 days on 15 days off.
- Iron (Ferrous Sulfate)- 25mg.
- After Breakfast: Take 20 days out of every month.
- Vitamin C-500mg
- Vitamin E-400iu
- Vitamin D3-400iu
Lunch
- Multivitamin. Take everyday.
-
Multi-mineral. Take 25 days of every month.
-
Calcium-1000mg,
-
Magnesium-400mg,
-
Zinc-25mg
-
Mid-Afternoon
- Vitamin B Complex. Take 15 days out of every month.
- Complex includes: B1- 15 mg, B2- 17 mg, Niacin- 200mg, B6- 20 mg, Folic Acid- 400 mcg, B12- 60 mcg, Pantothenic Acid- 100mg, Choline Bitartrate- 20mg, Inositol- 20 mg
- Vitamin B12- 500mcg. Take 15 days out of every month.








Dinner
-
If vitamin intake was not taking at lunch take them before dinner.
Night Time
Before Bed: Take 22 days out of every month.
- Arginine- 500mg
- Glutamine- 500mg
Supplements
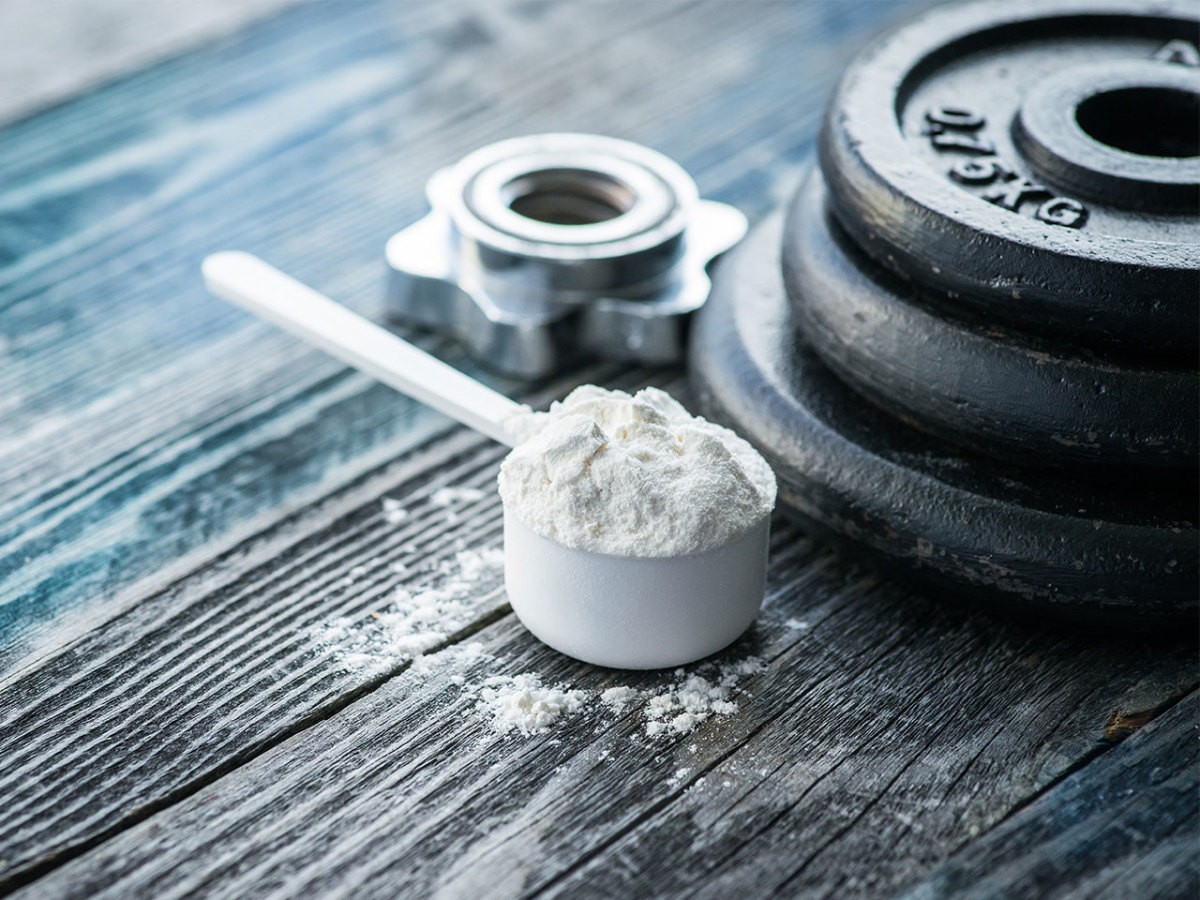
Caffeine
Caffeine is widely used in sports because it can improve both and anaerobic performance in trained and untrained individuals. When taken before or during exercise, caffeine has small to moderate-sized effects of lowering the rating of perceived exertion (RPE) and improving aerobic endurance, anaerobic power, sprint speed, muscle endurance, muscle strength, muscle power (jump height), and agility. It also improve cognitive functions, such as attention, reaction time, memory, and feelings of fatigue.
Dose: 3–6 mg per kilogram of bodyweight (approximately 200–400 mg in a 70 kg person), taken around 60 minutes before exercise.




Creatine
Creatine has been reported to reduce body fat and improve some measures of anaerobic exercise performance, strength, and power output.
Use only:
- Creatine Monohydrate
Dose: 3–5 g per day.
Whey or Soy Protein
Whey is a high-quality, well-absorbed source of protein with benefits that are similar to those of increasing protein intake in general, such as augmenting muscle gain when paired with resistance training, limiting muscle loss during low-calorie diets/aging, and modestly limiting fat gain during periods of excessive calorie intake.
- If following a plant based diet or are lactose intolerant, replace with Soy Protein supplement.
Dose: Optimal protein intake will vary depending on one’s unique goals. Refer to your personalize macro ratios.




Sodium Bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate before exercise has been found to enhance exercise performance, particularly during high-intensity activities lasting between 30 seconds and 12 minutes, during tests assessing muscular endurance.
Options are tablets or powder: Examples include: Baking Soda, Alka seltzer tablets, and some mineral waters including Club Soda.
Dose: approximately 0.3 grams per kilogram of body weight (g/kg) taken 1 to 3 hours before exercise.
Nitric Oxide: Tart Cherry Juice(Montmorency Cherry Juice)
To enhance exercise recovery or endurance exercise performance, tart cherry juice should be taken daily for 3–7 days before the exercise session of interest and 1–2 hours before exercise on the day of the event. To enhance exercise recovery, tart cherry juice should also be consumed 2–4 days following the event.
Dosages: 237 mL or 355 mL, consumed twice per day (474–710 mL total).






Carbohydrate Loading
Carbohydrate-loading protocol improved performance metrics during one-day endurance races.
Dose: Starting 6, 5, 4 days out from competition date, reduce carbohydrate intake to 50% or less with protein at 20-25% and fat at 30-40% respectively.
Then 3, 2 ,1 days out from competition, increase carbohydrate intake to 80% with protein at 8-12% and fat at 10-15% respectively.
Beta Alanine
Beta-alanine improves high-intensity exercise performance in events lasting 1–10 minutes.
Studies have found a range of 3.2–6.4 grams per day of beta-alanine to be effective for enhancing exercise performance.
Dosage: 0.8–1.6 grams of beta-alanine every 3–4 hours throughout the day for 2 weeks.


Macro Nutrient Meal Plan: Build Phase
Build Phase Macro Nutrient Meal Plan
Look to modify diet to equal these Macro ratios:
Carbs: 45-60%Protein: 15-20%
Fat: 25-30%





Super Water
Upon waking: : 6:00-7:15 am
Ingredients: 12-160z glass of water. In addition add all or any of the following: salt, squeeze of lemon, chia seeds, apple cider vinegar, & local honey
Breakfast
Within 45 minute upon rising look to consume breakfast. Breakfast options are:
Oatmeal would be the go to on tough or high volume days of training, Avocado toast would be consumes on rest days or low activity training days.










Coffee and Green Tea
With or around breakfast add liquid intake with:
1 Double Espresso or cup of Americano Coffee
and
1 cup 6-8oz of Green Tea
Training
Start training 1 to 2 hrs after finishing breakfast
(9:30-10:00am)
Consume liquids, bars, gels, gummies, dates, bananas, etc each hour of training according to your personalized activity burn rate.










Recovery Shake: Post Training
Consume immediately after completion of training. Options include:
Lunch
Lunch should be a balanced meal focused on carbohydrates during this phase of training.
Options include:
Bean Salad
Pasta with Vegetables









Afternoon Snack
Look to snack on some fruits and vegetables. Other snacks include, whole grain cereals, trail mixes including nuts and seeds.
Dinner
Diner should focus on a balance meal with a carbohydrate base and include a protein source and fat source.
Options include:
Budda Bowel
Rice and pasta dish with chicken and vegetables











Evening Snack
Evening snack must be consumed no later than 2 hrs before plan sleep time.
Snacks include:
Chia Pudding with toping
Protein Shake
Also, look to complete any macro nutrients deficinces that have not been complete for the day.
Liquids
In addition to consuming liquids during training and during meal times. Make sure to take in adequate amounts of water throughout the day.
Reference your personalized hydration schedule but in general look to consume 64-82 ox of water multiply times per day at 8-16oz increments.





Grocery List
Grocery List
Let's Go Shopping
Being prepared and have a plan when food shopping makes it easy and efficient to purchase the right food to fuel your active lifestyle.


Carbohydrates
Highest Nutrient DensityGood First Choice
- Whole Grains:
- wheat
- oats
- barely
- millet
- rye
- bulgur
- couscous
- polenta
- Buckwheat
- Quinoa
- Spelt
- Enriched Breads
- Rolls
- Tortillas
- Cereals
- Rice
- Pastas
- macaroni
- spaghetti
- Popcorn Kernels
Moderate Nutrient DensityReasonable Second Choice
- French Toast
- Pancakes
- Muffins
- Cornbread
- Crackers
- Cookies
- Biscuits
- Granola
- Waffles
- Presweetened Cereals
Proteins
Highest Nutrient DensityGood First Choice
- Legumes
- Lentils
- Chickpeas
- Hummus
- Beans
- Tofu
- Tempeh
- Soy Yogurt
- Beans
- Refried Beans
- Tofu
- Tempeh
Moderate Nutrient DensityReasonable Second Choice
- Fish
- Poultry
- Light meat
- dark meat
- no skin
- Whole Eggs
- Lean Meats
- fat-trimmed beef
- lamb
- pork
- Ham




Fats
Highest Nutrient DensityGood First Choice
- Avocado
- Olive Oil
- Peanut Butter
- Tahini
- Seeds:
- Flax
- Sesame
- Hemp
- Chia
- Sunflower
- Pumkin
- Nuts
- Almond
- Brazil
- Cashew
- Walnut
- Peanut
- Pistachio
Moderate Nutrient DensityReasonable Second Choice
- Coconut Oil
- Canola Oil
Fruits
Highest Nutrient DensityGood First Choice
- Apples
- Apricots
- Avocados
- Bananas
- Blueberries
- Cantaloupe
- Dates
- Grapes
- Grapefruit
- Goji Berries
- Guava
- Kiwi
- Lemonds
- Mangos
- Melons
- Oranges
- Papaya
- Peaches
- Pears
- Strawberries
- Plums
- Apples
- Bananas
- Pears
- Watermelon
Moderate Nutrient DensityReasonable Second Choice
- Canned or Frozen Fruit (in syrup)
- Sweetened Juices
- Dried Fruit
- Raisines
- Currants




Vegetables
Highest Nutrient DensityGood First Choice
- Bamboo Shoots
- Bok Choy
- Bean Spouts
- Broccoli
- Brussel Sprouts
- Cabbage
- Carrots
- Cauliflower
- Corn
- Cucumbers
- Eggplant
- Garlic
- Green Beans
- Green Peas
- Leafy Greens
- Spinach
- Kale
- Mustard
- Collard Greens
- Legumes
- Lettuce
- Mushrooms
- Okra
- Onions
- Peppers
- Potatoes
- Pumpkin
- Scallions
- Seaweed
- Snow Peas
- Soybeans
- Sweet Potatoes
- Tomatoes
- Water Chestnuts
- Winter Squash
- Yams
Other
Highest Nutrient DensityGood First Choice
- Plant Milks
- Soy
- Almond
- Oat
- Rice
- Plant Based Cheeses
- Herbs/Spices
- Cinnamon
- Turmeric
- Honey
- Applesauce
- Vinegars
- Balsamic
- Apple Cider
- White
- Baggs Liquid Aminos
- Nutritional Yeast
- Sea Salt
- Mineral Water